6 major causes of goiter
6 major causes of goiter
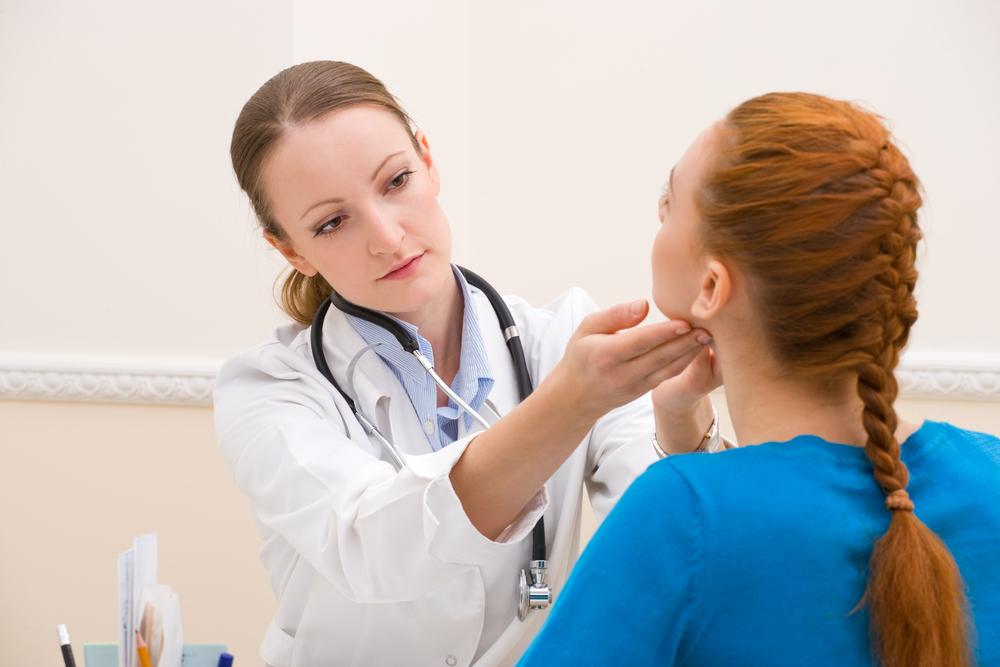
There are several glands in the body, each of which secretes hormones that aid essential bodily functions. Like every other part of the body, even these glands are prone to disorders. One such disorder that arises due to a malfunctioning thyroid gland is called goiter. This condition is characterized by an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland. In goiter, the thyroid, which is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck, swells abnormally and becomes visible. Goiter is often attributed to the lack of iodine in one’s diet, but there are other underlying health conditions that cause goiter as well.
Though goiter is not a life-threatening disease, goiter can make it difficult for the individual to swallow or breathe. Usually, the size of the goiter is what determines whether one needs immediate treatment for the same or they can go about their life as usual.
Read on to know more about goiter, as it will come in handy in identifying the disease and seeking timely help for the same.
Causes of goiter
Though goiter has been attributed to the lack of iodine in our diet, this condition is also caused by other underlying health conditions. The major causes of goiter are as follows:
- Grave’s disease – When the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, there are high chances of developing goiter. A major cause of goiter is Grave’s disease, where the antibodies produced by the immune system mistakenly attack the thyroid gland, and this results in the overproduction of the thyroxine hormone. This overstimulation is what causes the thyroid gland to swell.
- Hashimoto’s disease – An underactive thyroid gland can cause goiter as well. A health condition that causes the thyroid gland to produce less thyroxine is called Hashimoto’s disease. This autoimmune disease affects the thyroid gland’s ability to produce thyroxine, and the production reduces dramatically. When the pituitary gland senses a low hormone level, it produces more of the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) to stimulate the thyroid gland, and this causes the gland to swell.
- Iodine deficiency – Iodine deficiency has been hailed as a major cause of goiter. Not many are aware of the pivotal role iodine plays in the production of thyroid hormones. Iodine is primarily found in seawater and the soil in coastal areas, and it is significantly less in the inland areas or areas at high elevations. Which is why people living in these areas are more prone to goiter. The thyroid gland enlarges in an effort to obtain more iodine and the condition is made worse if people consume hormone-inhibiting foods like cabbage, cauliflower, and broccoli.
- Multinodular goiter – This condition leads to a gradual development of goiter. Multinodular goiter is a condition in which several solid or fluid-filled lumps called nodules starts developing on either side of the thyroid gland, causing overall enlargement.
- Solitary thyroid nodules – At times, a single nodule develops in one part of the thyroid gland. Usually, such nodules are noncancerous and only cause an enlargement of the thyroid gland.
- Inflammation – An inflammatory condition called thyroiditis causes pain and swelling in the thyroid gland. This can even cause an increase or reduction in the production of thyroxine.