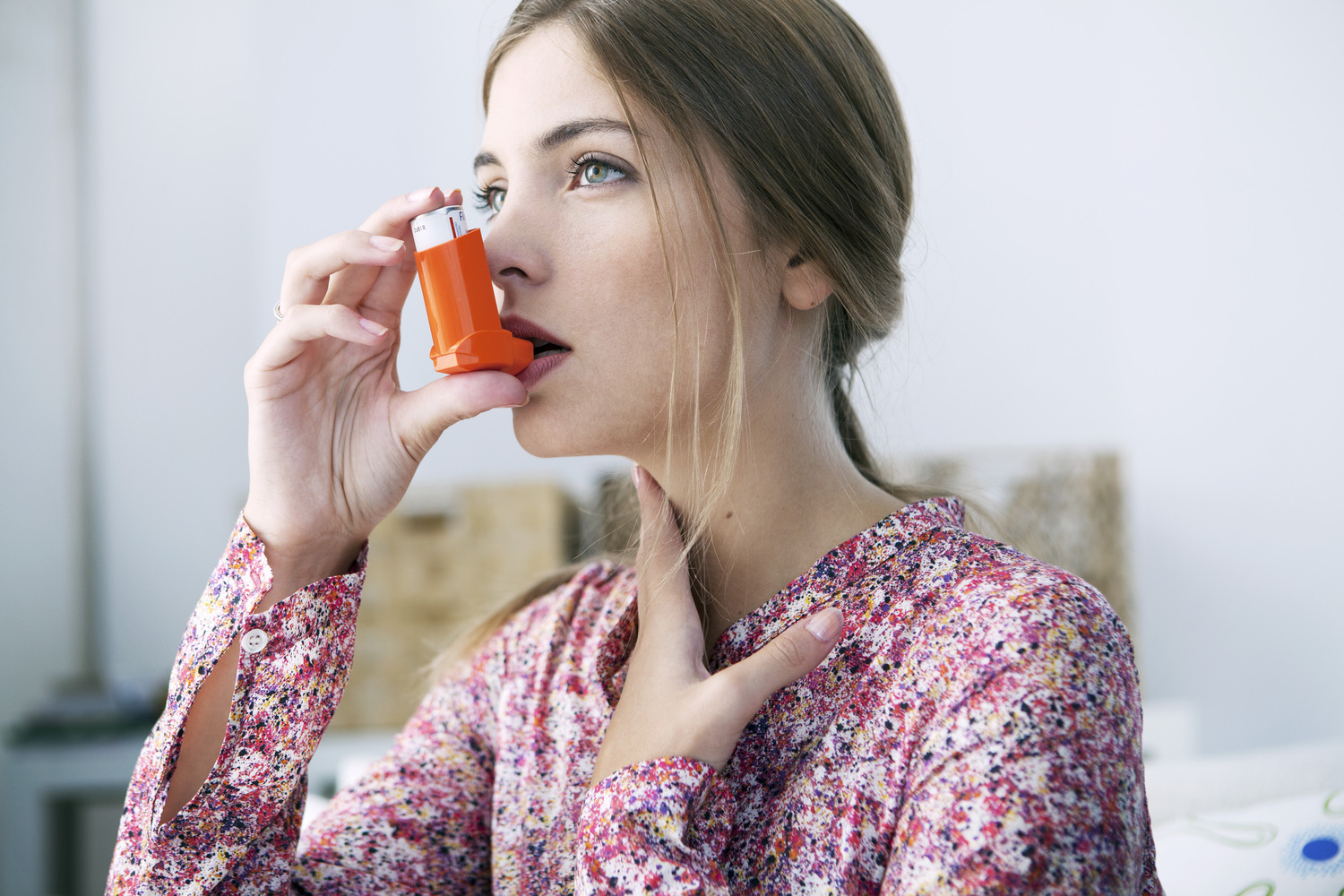
COPD vs Asthma: The Main Differentiating Factors
According to the World Health Organization, chronic respiratory diseases are the cause of around 6% of deaths each year, across the globe. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and chronic asthma are two of the most common respiratory disorders. The former is an umbrella term for progressive respiratory conditions such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema, whereas the latter is often mistaken as COPD, but is characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways in the lungs. Asthma is associated with allergies and can be treated by targeting inflammation and COPD is treated with bronchodilators, and in some cases by removing the risk factors.
Although both these conditions may be confused quite often, these are two distinct respiratory disorders and asthma is considered one of the risk factors for developing COPD. The symptoms of COPD and asthma seem similar. Shortness of breath, cough, and wheezing are the common symptoms in both these conditions. Moreover, airway hyper responsiveness, which is the condition of sensitivity while inhaling is also a common symptom observed in both COPD and asthma. Here are some of the distinguishing factors that differentiate COPD from chronic asthma:
- Age
Asthma is a common respiratory disorder among children and as per the WHO estimates, more than 235 million people in the world are currently suffering from the condition. According to the National Institutes of Health, COPD is usually diagnosed in adults over the age of 40 years. The condition is also common among those who are former or current smokers. - Triggers
There is a difference between the triggers that cause asthma and COPD. Some of the various triggers that aggravate the condition of asthma are:
- Cold air
- Allergens
- Physical exercise
- Anger or fear
- Certain medications such as anti-inflammatory medications
The condition of COPD is worsened by infections of the respiratory tract infections such as the flu and pneumonia. Moreover, environmental pollutants also aggravate COPD.
- Causes
The primary cause of asthma is unknown and not completely understood. The strongest risk factor that may cause chronic asthma is considered to be a combination of particles that may provoke allergy or irritation and genetic predisposition with exposure to environmental substances. These allergens are pollens or molds, indoor allergens such as pet dander and house dust mites, tobacco smoke, and air pollution, to name a few. Moreover, urbanization is also considered to be a cause of asthma, but the exact association is unclear. The most common cause of COPD is smoking, which amounts to 9 out of 10 deaths caused by COPD. Another cause of the condition is exposure to fumes from burning fuel. Smoking irritates the lungs, which leads to loosening of the elasticity of the air sacs and they over expand. This traps the air in the lungs during exhaling. Also, around 1% of the people with COPD develop the condition due to a genetic disorder caused due to the low levels of alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT), a protein found in the liver.
It is highly recommended to consult the doctor once any of these symptoms are observed. Taking the note of the differences between COPD and chronic asthma helps one to understand the condition better.